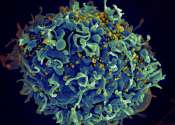
HPV discovery yields breakthrough in understanding protein activity
A new study led by Yale scientists shows that the activity of a portion of a human papillomavirus (HPV) protein does not depend on its amino acid sequence or composition. This discovery challenges the widely held belief that ...