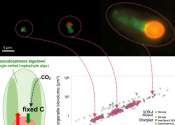
Decoding the language of cells: Profiling the proteins behind cellular organelle communication
In cellular biology, unraveling the complexities of cellular function at the molecular level remains a paramount endeavor. Significant scientific focus has been placed on understanding the interactions at organelle contact ...